In today’s fast-evolving manufacturing world, repmold stands out as a powerful tool that helps create high-quality, consistent parts quickly and efficiently. But what exactly is repmold, how does it work, and why does it matter so much across so many industries? This article provides a clear, easy-to-understand overview of repmold, its history, uses, materials, innovations, challenges, and future potential.
What is Repmold?
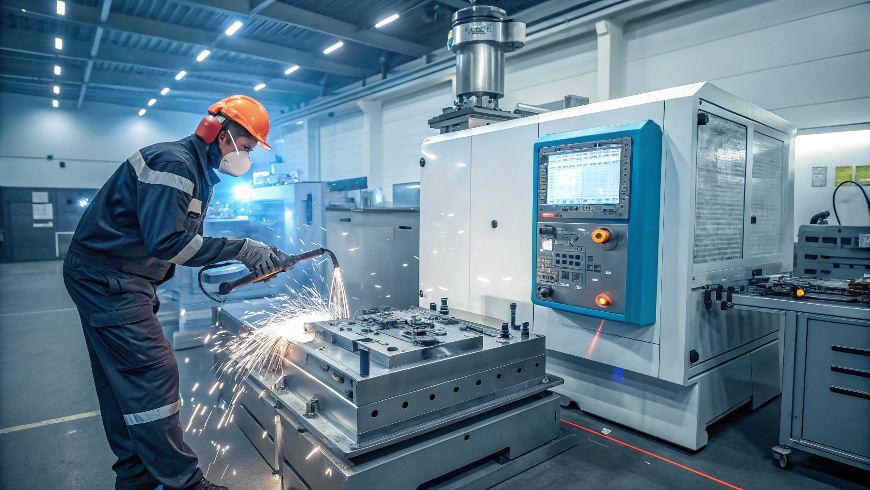
The word repmold comes from combining “replication” and “molding.” It refers to a specialized molding process used to produce identical parts by repeatedly forming materials—like plastic, metal, or composites—into a mold or cavity. After the material is injected or cast into the mold, it hardens into the desired shape.
Repmold plays a crucial role in mass production, helping companies make large quantities of parts with precision and uniformity. Without repmold, industries such as automotive, packaging, electronics, and medical devices would struggle to meet demand and maintain consistent quality.
A Brief History of Repmold
Molding technologies date back thousands of years, with ancient civilizations using simple molds for weapons, pottery, and jewelry. However, modern repmold evolved during the Industrial Revolution, when machines capable of shaping metal or plastic needed more precise molds.
The mid-20th century brought breakthroughs like injection molding, allowing factories to mass-produce parts with high accuracy. Today, repmold leverages digital tools such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and 3D printing to design and produce molds faster and more efficiently than ever before.
Common Uses of Repmold
Repmold is extremely versatile and finds uses in:
- Automotive parts: Engines, dashboards, plastic clips, and many vehicle components.
- Packaging: Bottles, containers, caps, and various packaging designs.
- Medical devices: Syringes, implants, face shields, and sterile tools.
- Electronics: Phone and laptop cases, connectors, and small device components.
By combining accuracy and speed, repmold ensures products used daily are safe, reliable, and affordable.
Materials Used in Repmold
The choice of materials for molds depends on production needs:
- Steel: Renowned for strength and durability, ideal for high-volume production molds.
- Aluminum: Lighter and easier to machine, best for short production runs or prototypes.
- Copper alloys: Excellent heat conductors to speed up cooling and production rates.
In addition, mold surfaces may be coated to fight wear and corrosion, extending mold life and maintaining part quality.
Why Repmold Matters in Everyday Life
Though most consumers never see molds directly, repmold impacts everyday life profoundly. From the toothbrush used each morning to the smartphone in your hand, repmold ensures that parts are consistent in quality, safe, and affordable due to mass production efficiencies.
Repmold also helps keep production costs low, making products accessible to more people worldwide.
Environmental Benefits of Repmold
Sustainability is a growing concern for manufacturers. Repmold supports eco-friendly production by reducing waste—molds designed with precision minimize excess raw material scraps. Many repmold processes also facilitate recycling by using moldable biodegradable materials.
Energy-efficient cooling systems and optimized production cycles reduce factories’ carbon footprint. As industries push toward greener operations, repmold technology aligns well with these goals.
Technological Innovations in Repmold
Repmold continues to evolve thanks to emerging technologies:
- 3D printed molds: Rapid prototyping allows molds to be created and tested faster.
- Smart molds: Embedded sensors monitor real-time temperature and pressure, improving accuracy.
- Simulation software: Virtual testing detects and resolves design flaws before production.
These innovations improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enable more complex product designs.
Challenges Faced by Repmold
Despite its advantages, repmold has challenges:
- Cost: High initial investments are often needed for precise mold tooling and skilled labor.
- Wear and Tear: Molds degrade with use, requiring regular maintenance and costly replacement.
- Environmental impact: While improving, some repmold processes consume significant energy.
Addressing these challenges is important for maximizing repmold’s benefits sustainably.
The Economic and Social Role of Repmold
Repmold drives economic growth by enabling mass production of affordable goods. It supports jobs in design, engineering, machining, and factory work worldwide. Training programs help prepare new generations to work with repmold technologies, underpinning manufacturing industries globally.
Its contributions extend beyond economics, influencing quality of life by making essential products widely available.
The Future of Repmold
Looking ahead:
- Scientists explore biodegradable mold materials for safer production.
- AI-powered design tools promise faster, error-free mold creation.
- Robotics may automate mold maintenance, improving factory efficiency.
- Industries needing renewable energy devices, medical tools, and high-tech gadgets will increasingly rely on repmold.
Repmold is set to remain a foundational technology supporting manufacturing’s evolution.
Conclusion
Repmold is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, blending tradition with digital innovation to deliver precision, speed, and cost-efficiency. Its versatile use across industries, combined with ongoing technological advances, makes repmold indispensable for producing the everyday products people rely on. Understanding repmold reveals why it quietly powers much of the world’s economy and why its future is closely tied to sustainability and smart manufacturing.
Visit Theinstanderofficial.com